Window covers are articles added to existing windows to enhance the energy efficiency, lower glow or true-to-life lighting, deliver privacy, or improve the impression or convenience of a home. Window veils include interior shades and drapes, plastic films straight to the glass, exterior shades, shutters, awnings and storm windows.
About 30% of a home’s heating power is lost via windows. About 76% of the daylight that drops on traditional double-pane windows evolves to be heated in colder seasons. Window covers can assist with this energy defeat and lower energy bills. The exact savings will count on the type of passion, the season, the environment, and how the attachment is used. In addition to the window covers, storm windows with Low-E layers and multi-layer glazing enhance the thermal version of windows and decrease solar heat yield.
INTERIOR WINDOW COVERING
- CURTAINS AND DRAPES: Curtains are internal fabric covers sized to fit the window, whereas drapes approximate the floor. A drapery’s capability to decrease heat loss and growth relies on several elements, including fabric style and shade. It isn’t easy to generalize their energy commission with such a wide assortment of curtains known. It would help close drapes on windows to obtain direct sunlight during summer to control heat gain. Investigations indicate that medium-colored curtains with white plastic support can decrease heat growth by 33%.
- WINDOW FILMS: Window films allow coalition against solar heat growths and guard against glare and ultraviolet direction. They are generously used in climates with long cooling seasons because they also stop the sun’s heat in cold weather. They can be helpful to homeowners who don’t want to stop views with other window remedies but have problems with glare and solar heat boost. They can also be the right option on windows that are challenging to work with other window therapies or in areas where painting, furnishing, or carpeting could be flagged by UV frontage.
Films mainly have three coatings: an adhesive coating that models against the mirror, a polyester film coating, and a scratch-resistant layer. You may also choose shades, UV blockers, or more dense films that offer protection. Low-e films are also appearing as an energy-saving alternative. Window films are ranked by the National Fenestration Rating Council (NFRC), which assembles window labeling and ratings for clients. ‘
The significance of these thoughtful films relies on the size of the window glazing area, window orientation, climate, building orientation and whether or not the window has internal insulation. There are also window films with Low-E layers, which can decrease winter heat loss and improve the thermal convenience of residents. They also usually help reduce near IR solar radiation. Window films can be professionally laid by a skilled installer or are known for do-it-yourself tasks at home advancement shops. Window films need extra maintenance for cleaning. They can harm protected glazing unit stamps if they mainly soak solar radiation. Most window works will cancel their contracts if the film is established on one.
EXTERIOR WINDOW COVERING
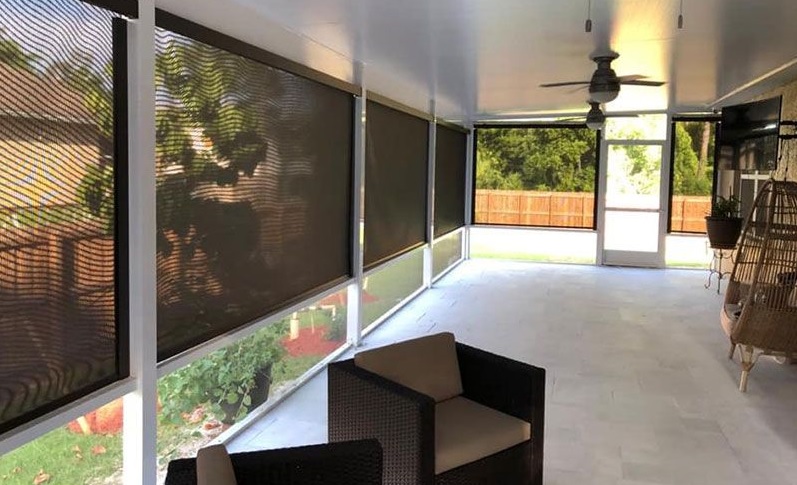
- EXTERIOR SHUTTERS AND SHADES: Exterior shutters and shades are distinct materials, including fabric, wood, steel, aluminum, or vinyl. They are most useful at decreasing solar heat yield. Shades are generally fabric or vinyl, and the material may have gaps that permit some visibility via the window. The bigger the entrances, the less shield from solar growth. They are usually manually managed, though some can be extended or completed with a crank inside the home.
- EXTERIOR SOLAR WINDOW SCREENS: Solar nets can decrease solar heat growth, UV wear, and glow. They can be established on the interior or exterior as roller tints or fixed meetings, and they generally qualify for a picture out the window and sunlight information. They look identical to traditional insect meshes but provide more efficiency advantages. The exposure factor on solar nets changes and influences the efficiency advantages; greater exposure decreases the defense against glow and solar heat growth but improves visibility and light dispatch.